C. Kluft1, J. Begieneman1, F. Ataullakhanov2,3, S. Talens1
1Good Biomarker Sciences, Leiden, the Netherlands; 2Dmitry Rogachev National Research Centerof Pediatric Hematology, Oncology and Immunology, Moscow, Russia; 3Center for Theoretical Problems of Physicochemical Pharmacology, Moscow, Russia
Introduction
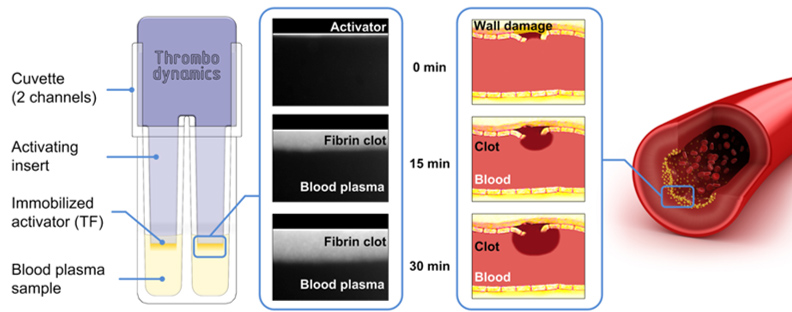
Thrombodynamics is a new pharmacodynamic test system for coagulation. Clot growth and thrombin wave patterns in space are documented with a video-microscopic system with a fluorogenic thrombin substrate. Coagulation is activated by immobilized tissue factor with a density resembling cell-bound tissue factor.

Aim
The aim of the study was to test thrombodynamics in haemophilia patients
Materials and Methods
Thrombodynamics analysis is performed in factor FVIII, FIX and FXI deficient plasma. Factor deficient plasma is mixed with normal pool plasma or suppleted with different coagulation factor concentrates. The following FVIII concentrates were tested; Advate® (recombinant octocog alfa, Baxter), Haemate® (plasma-derived FVIII plus vWF, CSL Behring), Elocta® (recombinant Fc-fusion, efmoroctocog alfa, SOBI), Bay94® (pegylated recombinant FVIII, Bayer). The following FIX concentrates were tested; Immunine® (plasma-derived FVIII, Baxter), Refixia® (pegylated recombinant nonacog beta pegol, Novo Nordisk), Alprolix® (recombinant Fc-fusion eftrenonacog alfa, SOBI). The effect of inhibitors on the different factor concentrates were analyzed by addition of FVIII inhibitor (4BU/ml, Affinity Biologicals) or FIX inhibitor (2.5 BU/ml, Affinity Biologicals). From thrombodynamics analysis we analyzed the following parameters; clot size at 30 minutes (µm), the stationary clot growth (Vst, µm/min) and the growth rate at 5000s (µm/min).
Results
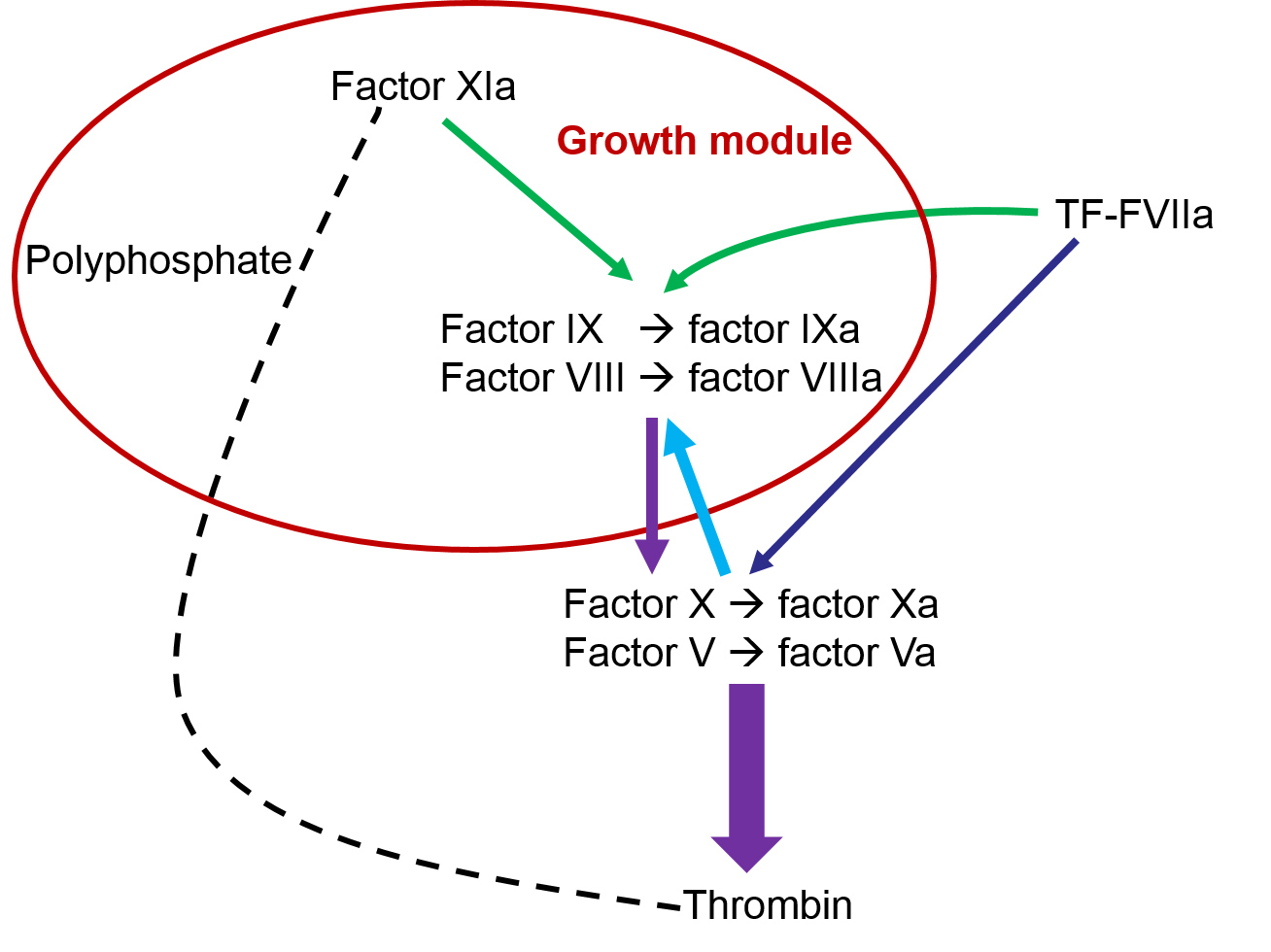
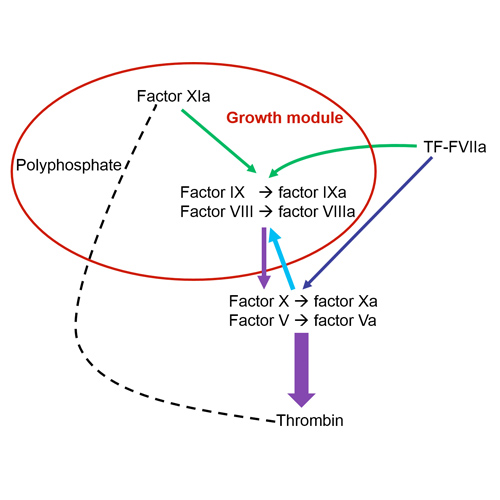
Fig 1: The growth module of thrombodynamics. Schematic representation of the coagulation factors involved in thrombodynamics analysis.
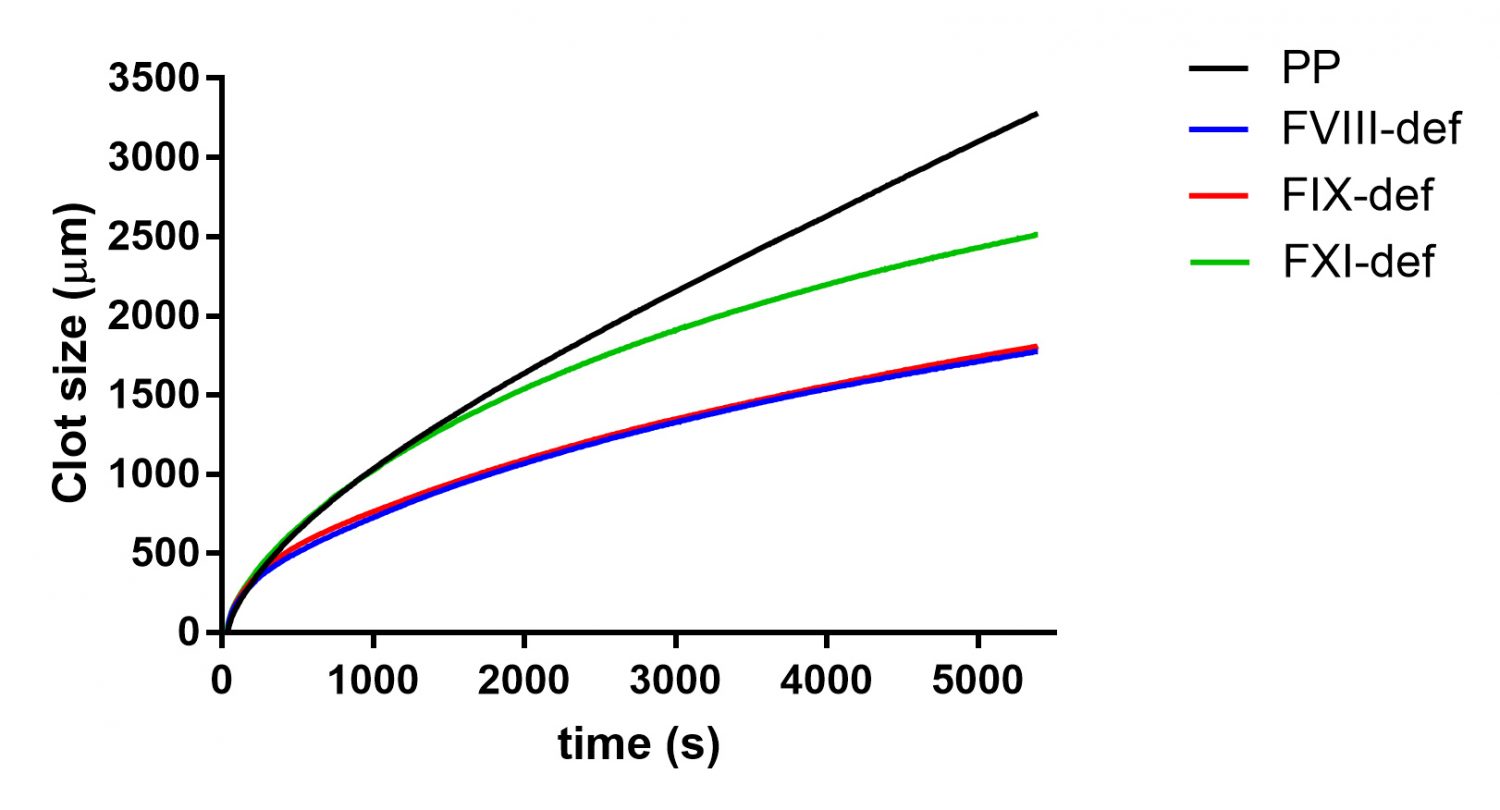
Fig 2: Thrombodynamics analysis of clot growth of FVIII, FIX and FXI-deficient plasma compared with normal pool plasma.
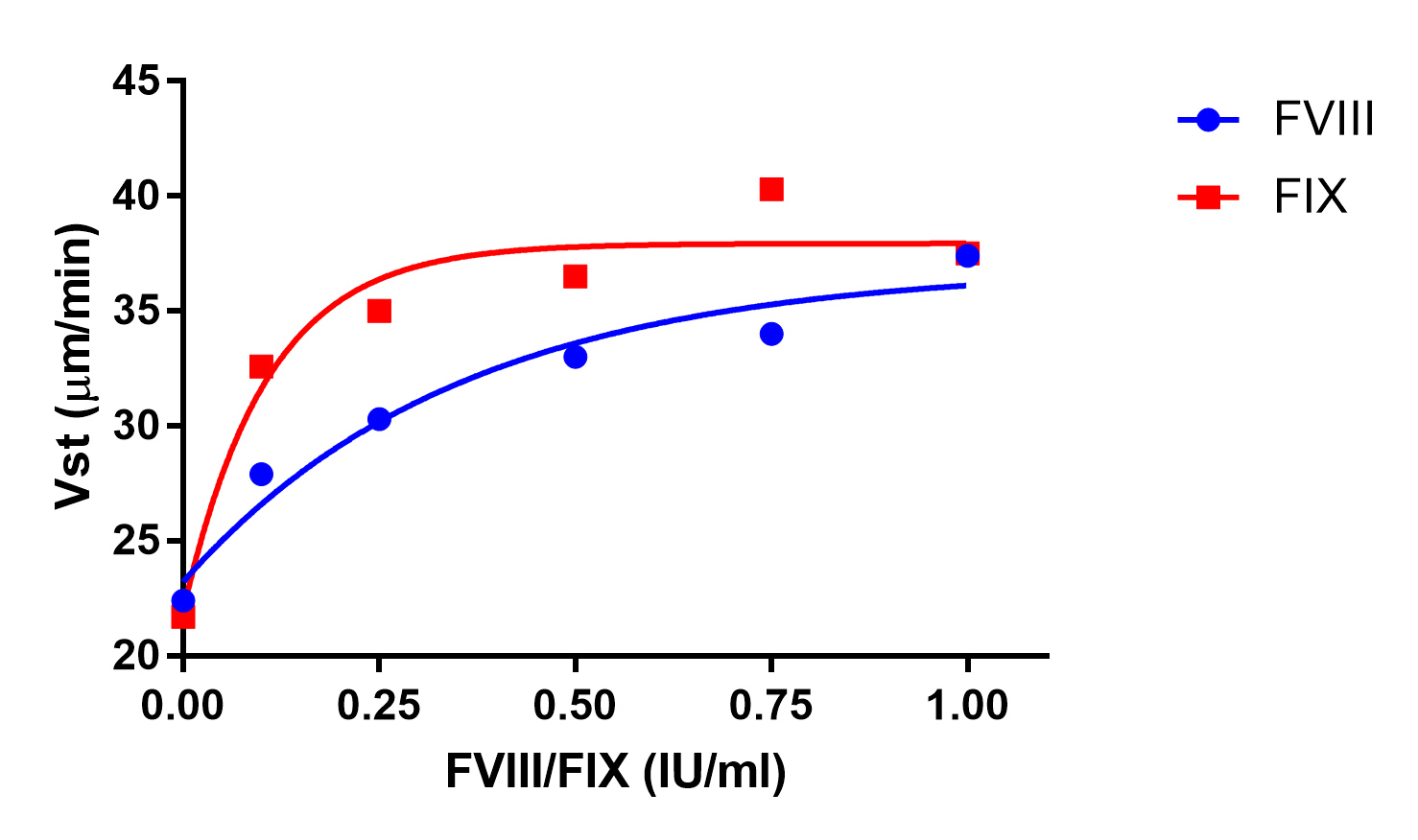
Fig 3: Clot growth rate (Vst) in plasma with different FVIII and FIX levels. These levels are obtained by mixing pool plasma with factor deficient plasma
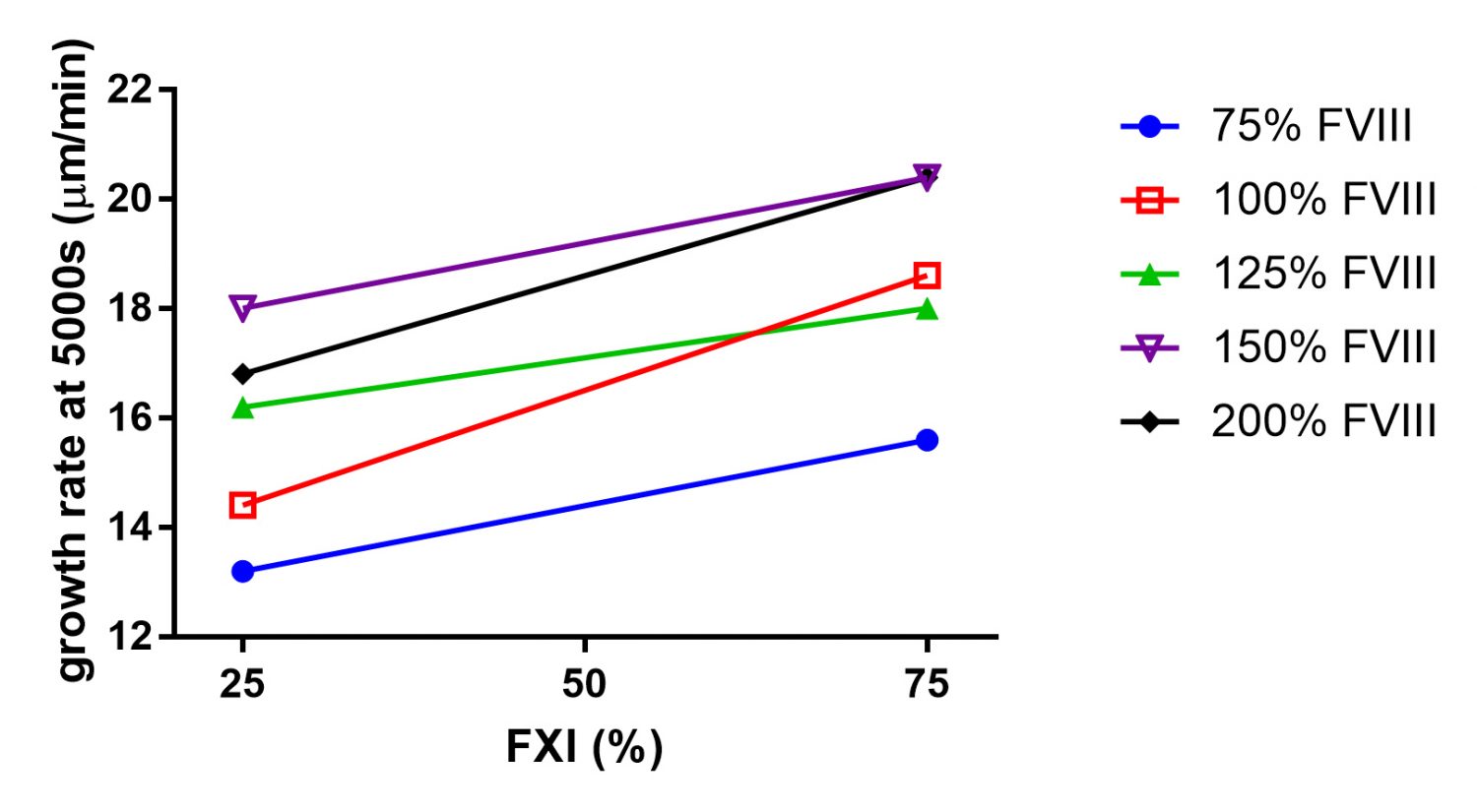
Fig 4: Clot growth rate at 5000 s (µm/min) in plasma with different FVIII (75 – 200%) and FXI (25 and 75%) levels.
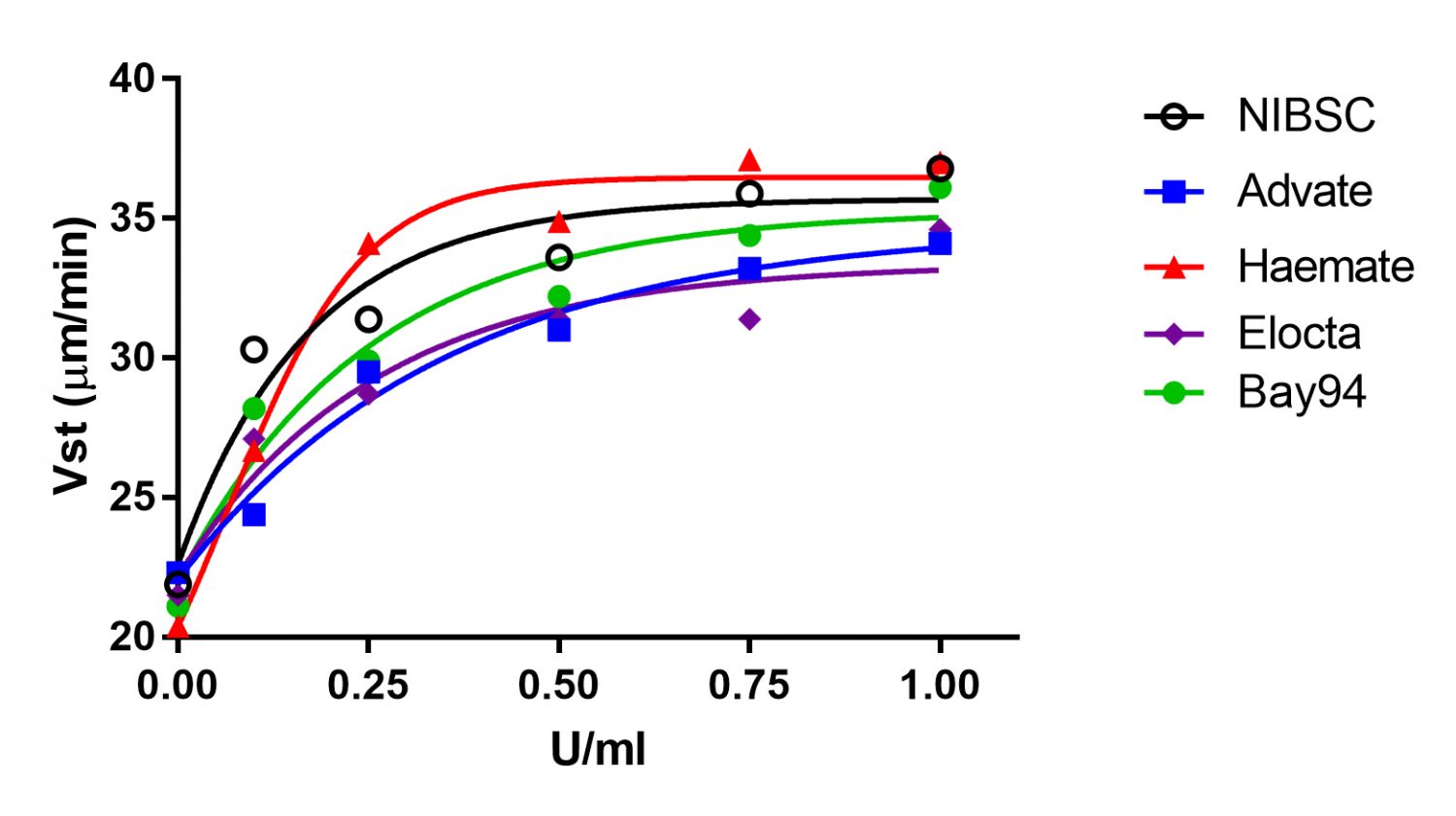
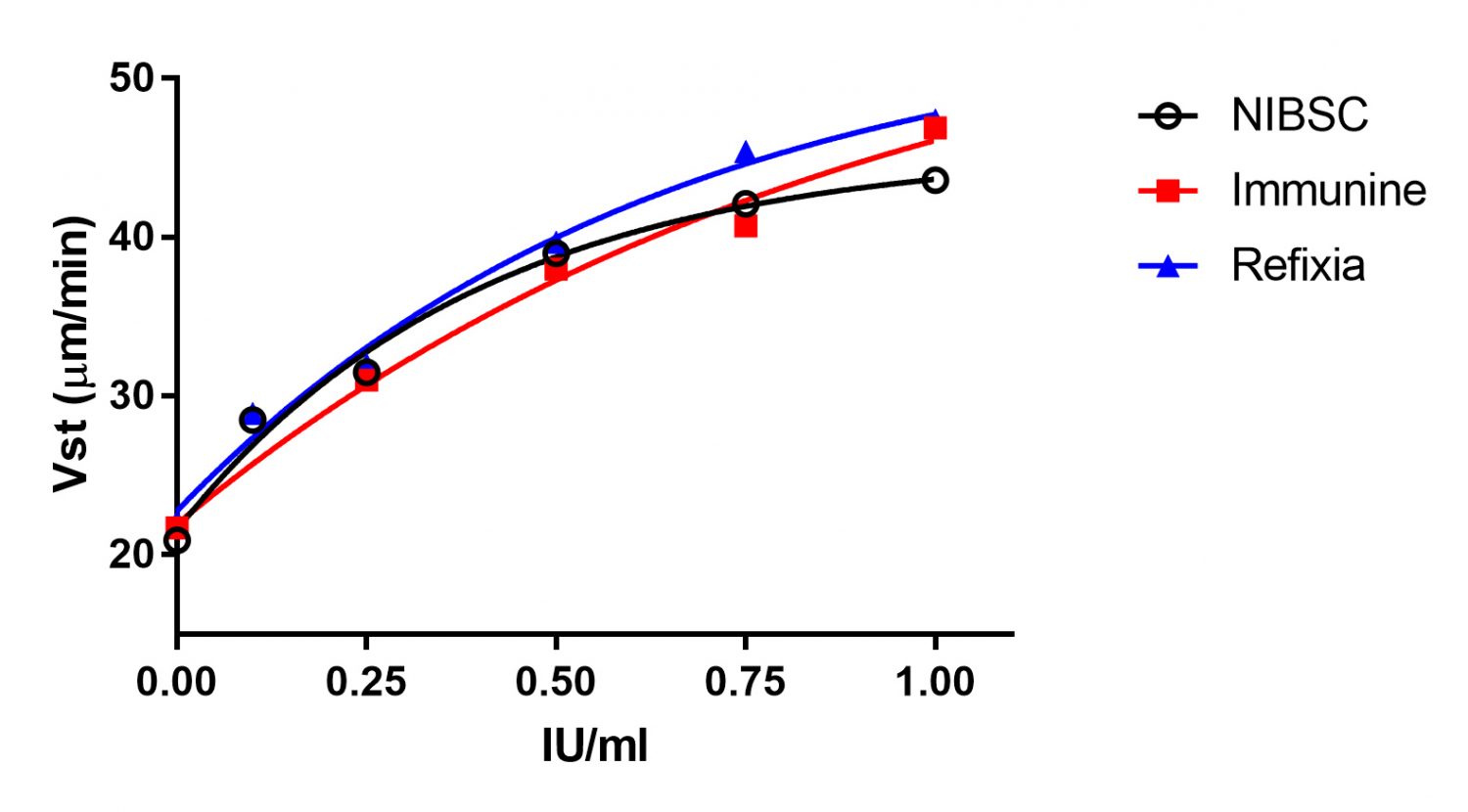
Fig 5: Clot growth rate (Vst) of different FVIII preparations (0 – 1 U/ml) in FVIII deficient plasma (left image) or different FIX preparations (0 – 1 U/ml) in FIX deficient plasma (right image).
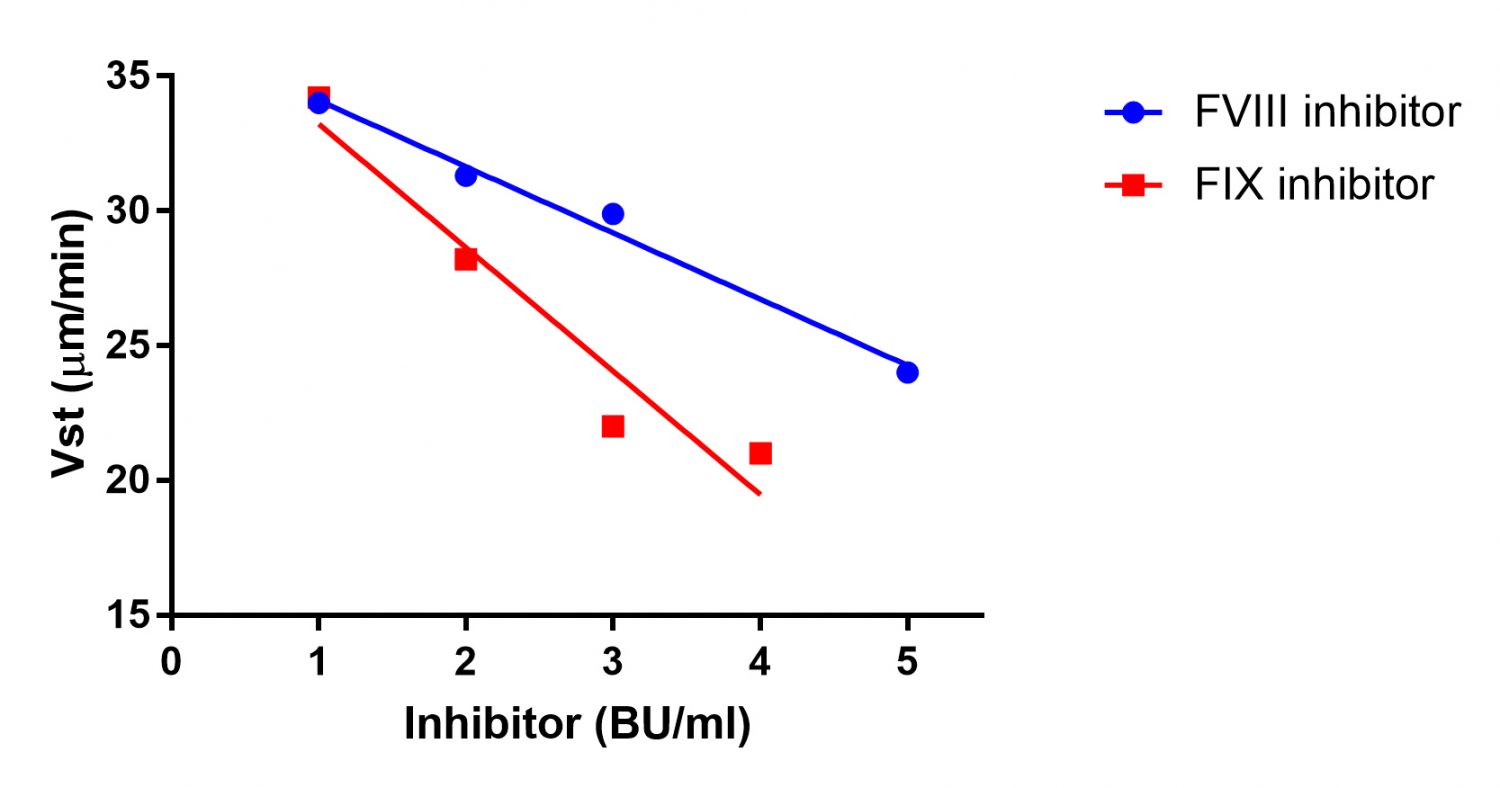
Fig 6: Clot growth rate (Vst) in plasma with FVIII and FIX inhibitors (1-5 BU/ml).
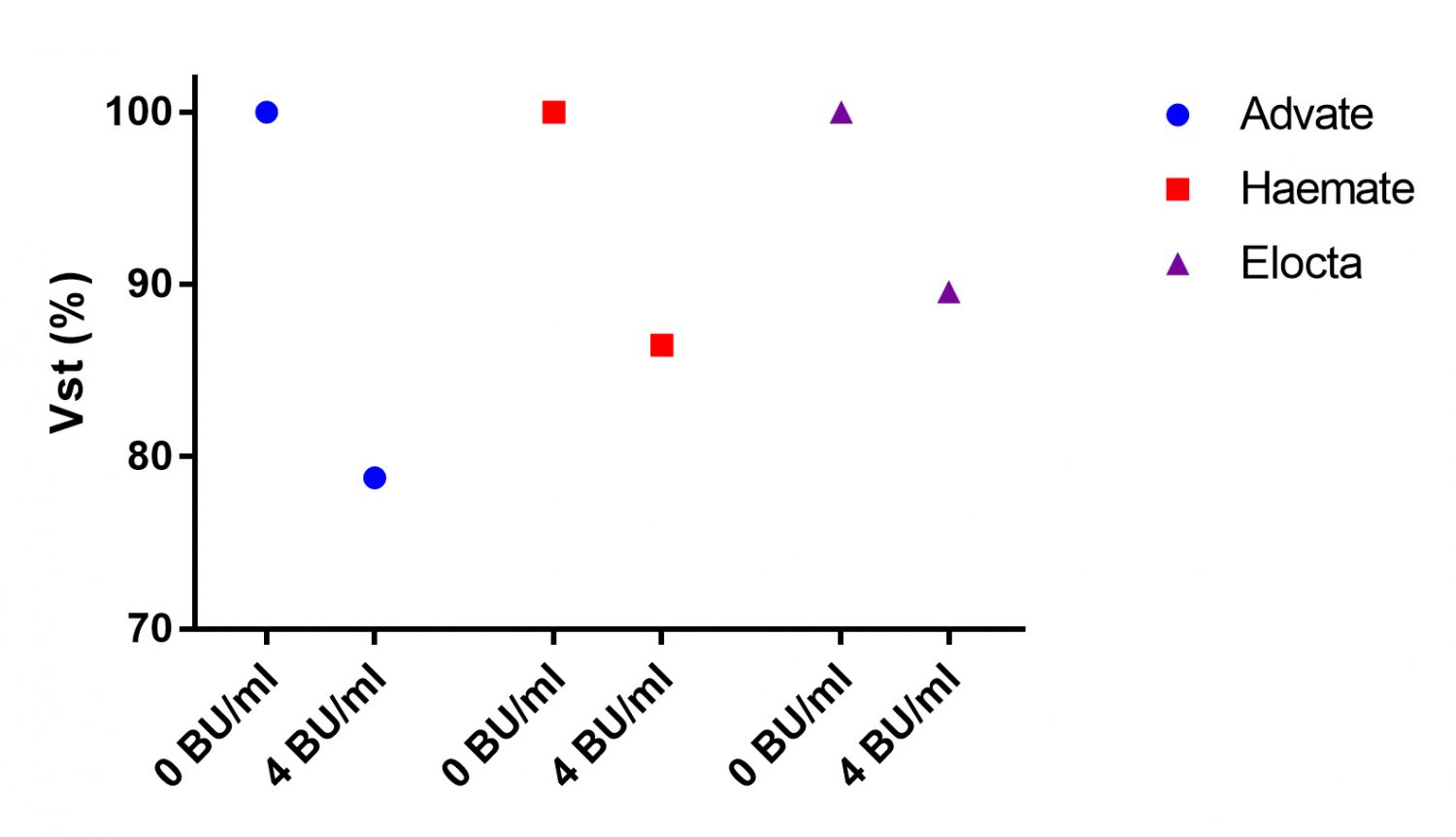
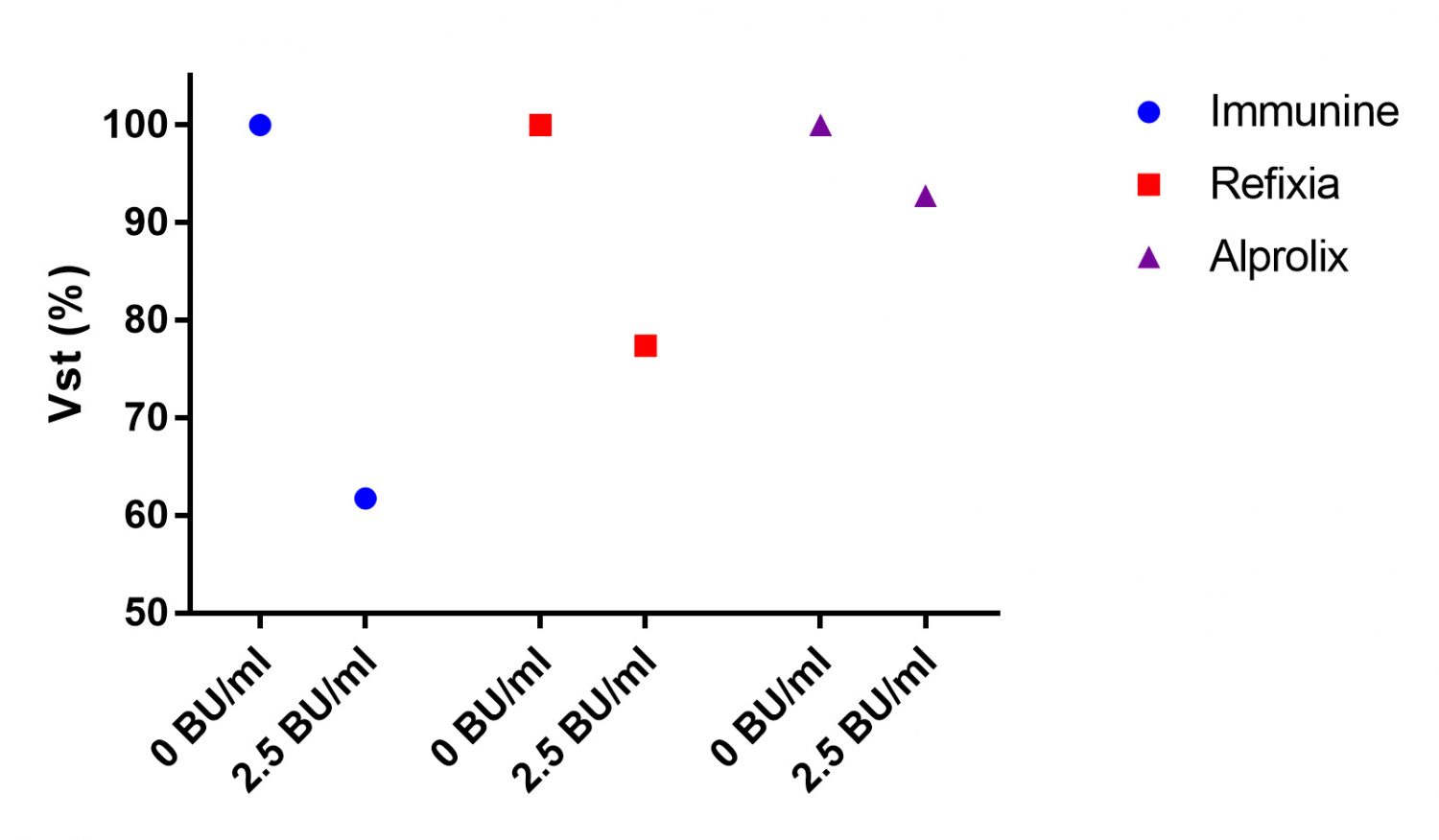
Fig 7: The effect of FVIII inhibitor (4 BU/ml) on different FVIII preparations (1 IU/ml) (left) and FIX inhibitor (2.5 BU/ml) on different FIX preparations (1 IU/ml) (right). The Vst of plasma without inhibitor is set at 100%.
Conclusions
- FVIII, FIX and FXI contribute to clot growth and therefore clot growth may be a better analysis tool then separate factor analysis in hemophilia.
- Plasma derived and recombinant FVIII and FIX concentrates in deficient plasma show similar clot growth.
- Fc-fusion FVIII and FIX products may be less inhibited by acquired inhibitors compared to other recombinant or plasma derived products.
Contact

website: www.gbsleiden.com
email: kluft@kluft.in