Charlotte Dekimpe1, Aurélie Dewaele1, Edwige Tellier2, Gilles Kaplanski 2, Nick Geukens3, Simon F. De Meyer1, Karen Vanhoorelbeke1,3
1Laboratory for Thrombosis Research, IRF Life Sciences, KU Leuven Campus Kulak Kortrijk, Kortrijk, Belgium; 2Aix-Marseille Université, INSERM, Vascular Research Center of Marseille, Unité Mixte de Recherche en Santé 1076, Marseille, France; 3PharmAbs, The KU Leuven Antibody Center, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
Introduction and Aim
Determination of ADAMTS13 activity, antigen and anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies is needed for the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of the rare disease thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) (Figure 1). ADAMTS13 parameters are, however, not always available on demand as current assays are complex and therefore only performed in expert centers and when multiple samples are available. Our goal is to develop fast and easy-to-use ADAMTS13 assays that allow single sample measurements using the fiber-optic surface plasmon resonance (FO-SPR) technology (White Fox 1.0 device). In this study we aimed at developing the FO-SPR anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibody assay (Figure 2).
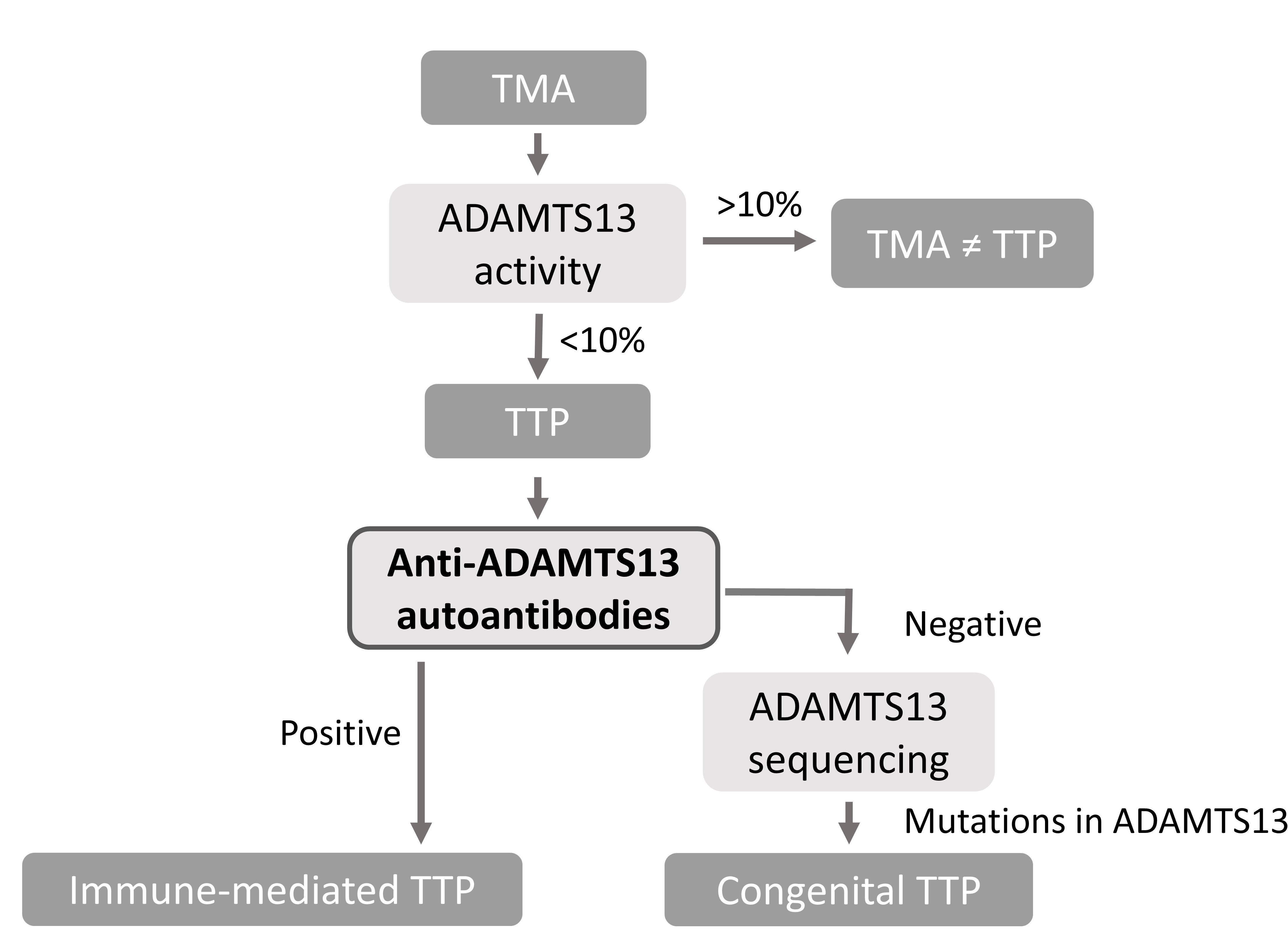
Figure 1: Flow-chart for the diagnosis of TTP.
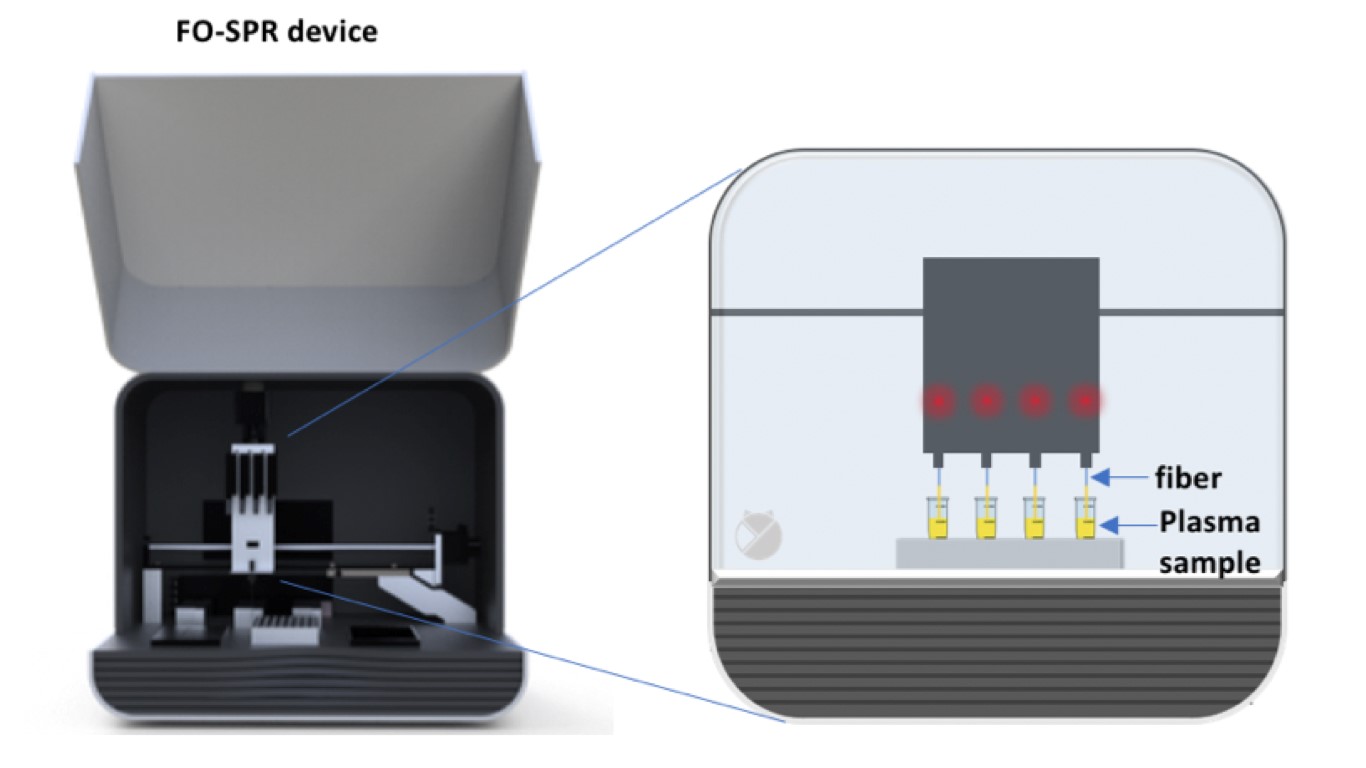
Figure 2: The fiber-optic surface plasmon resonance device.
Methods

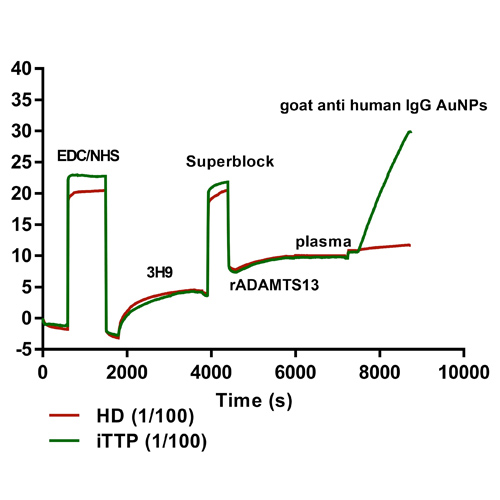
Figure 3: (A) Set-up anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibody ELISA. Patient anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies are binding to coated recombinant (r)ADAMTS13 and detected by HRP-labeled anti-human IgG antibodies. (B) Set-up FO-SPR anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibody assay. 3H9 is covalently coupled to the FO-SPR fiber using EDC/NHS chemistry, followed by a blocking step with superblock. rADAMTS13 is captured by 3H9 and allows binding of patient anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies, followed by signal amplification via goat anti-human IgG coupled gold nanoparticles. (C) Read-out FO-SPR anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibody assay. The SPR shift in function of time of the complete FO-SPR anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibody assay. The signal amplification SPR shift (goat anti-human IgG gold nanoparticles binding) is the final read-out of this assay.
Results
(1) Signal amplification with goat anti-human IgG conjugated gold nanoparticles
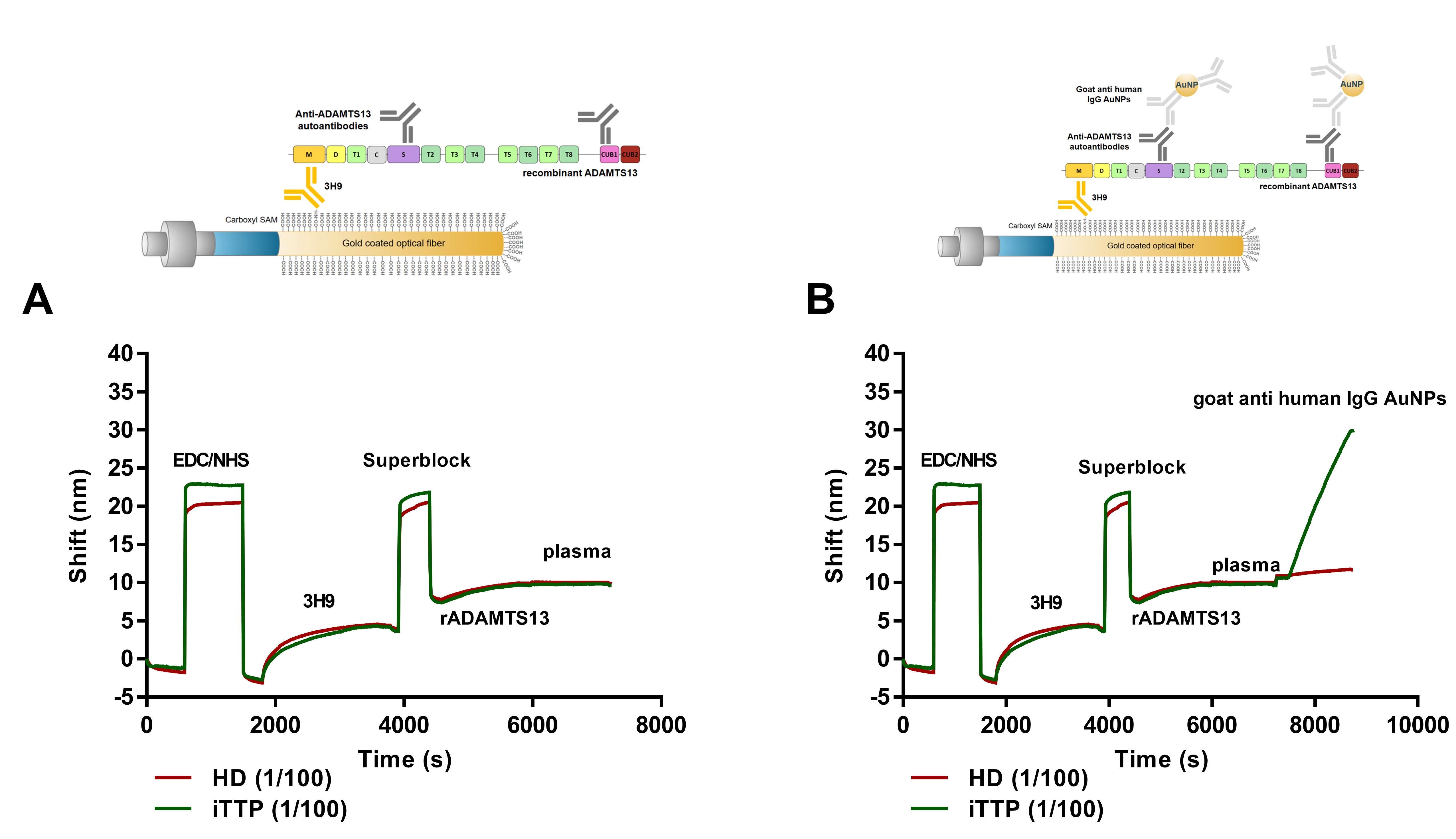
Figure 4: Label-free versus sandwich-detection method. The SPR shift in function of time of the FO-SPR anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibody assay. (A) Label-free detection method. There is no difference in SPR-shift observed after addition of iTTP patient plasma (1/100) or healthy donor plasma (1/100). (B) Sandwich detection method. Signal amplification was obtaining using goat anti-human IgG AuNPs.
(2) Immobilization of recombinant ADAMTS13

Figure 5: Optimization of recombinant ADAMTS13 concentration. The mouse anti-human ADAMTS13 antibody 3H9 was covalently coupled to carboxyl self-assembling monolayer gold-coated optical fibers using EDC/NHS chemistry. After blocking (SuperBlockTM), rADAMTS13 was captured. Different concentrations (0.5 – 1 – 5 µg/mL) of rADAMTS13 were tested. A high titer iTTP plasma sample was used for optimization. (A) FO-SPR shift (nm) after recombinant ADAMTS13 immobilization. (B) FO-SPR shift (nm) after signal amplification with goat anti-human IgG AuNPs. A rADAMTS13 concentration of 0.5 µg/mL was used for further experiments.
(3) Assay performance characteristics

Figure 6: Calibration curve.The calibration curve was established using different dilutions of a high titer iTTP plasma sample (set at 100%) (n=3). The detection limit (DL) of the assay was determined by performing repeats of a healthy donor sample. The DL (3xSD above mean of HD signal) was 0.03% (1.14% when taking into account the 1/40 plasma dilution) (red dotted line). The inter-assay %CV was assessed by performing four repeats of one iTTP sample (12.49%).
(4) Evaluation of the FO-SPR assay with iTTP plasma samples
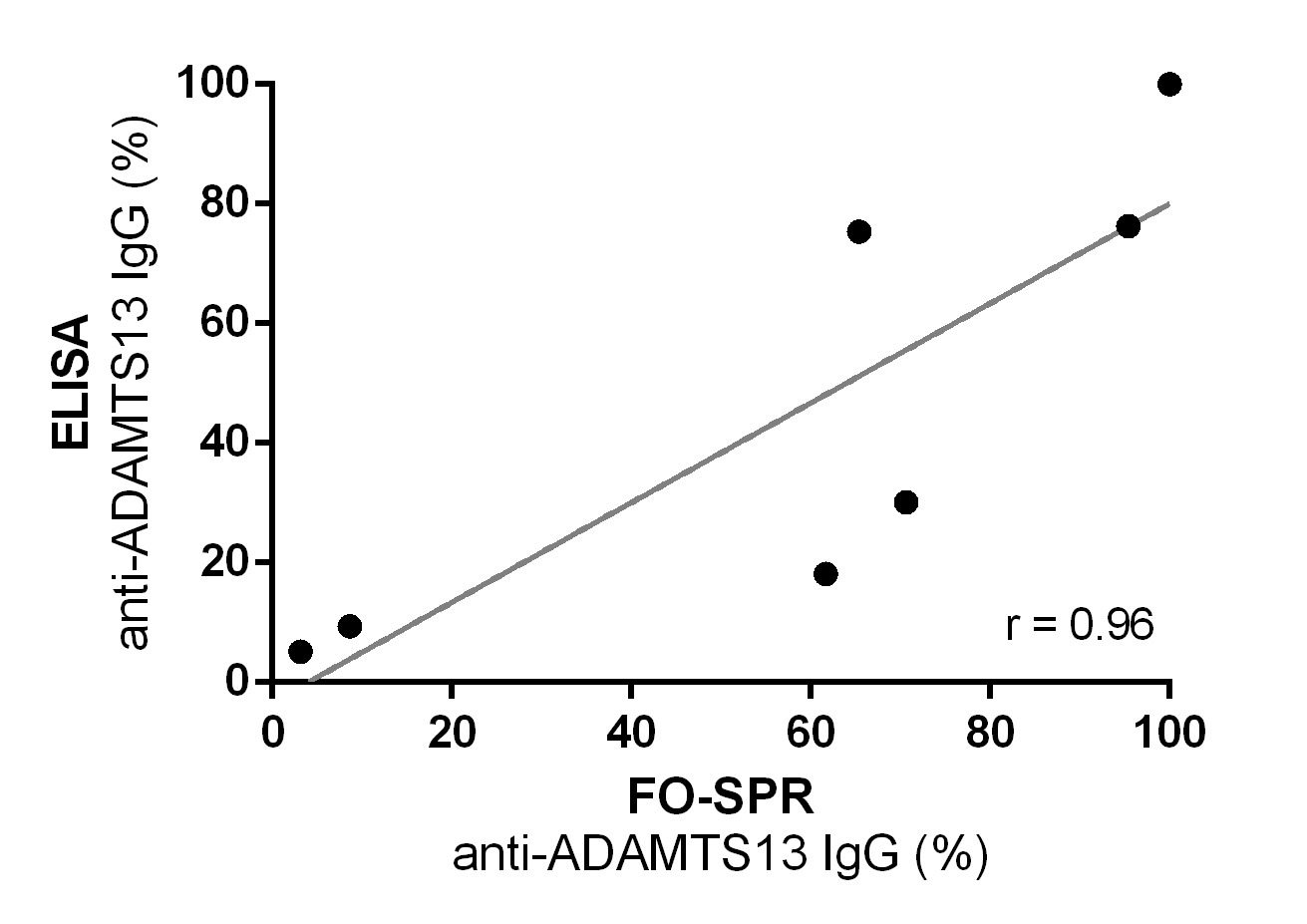
Figure 7: Correlation between anti-ADAMTS13 IgG titers measured using our FO-SPR assay or ELISA. Anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibody titers were determined in seven iTTP plasma samples using both our FO-SPR assay and our in-house ELISA. Anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibody titers (ranging from 3.16 to 95.40 %) obtained via FO-SPR showed significant correlation with titers obtained in ELISA (p < 0.05, r = 0.96).
Conclusions
A new FO-SPR anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibody assay has been established, which allows fast and easy single sample measurements. We are currently developing the ADAMTS13 activity and antigen assays on this device.